Stress echocardiogram – What is it?
A large number of patients with coronary artery disease may do not always present with symptoms when at rest. However, these may become manifest when the patient exert themselves e.g. taking a walk, climbing up a flight of stairs etc. During exercise, the heart arteries dilate so that more blood may be supplied to the heart muscle. However, when the arteries are narrowed due to disease, they do not dilate sufficiently, resulting in parts of the heart muscle not receiving adequate blood supply. Due to this, that particular part of the heart muscle may not move very well under stress, and this can be visualised on an echocardiogram.
Preparing for the test
The recommendations are similar to the ones advised prior to performing an exercise test. In a nutshell:
• Avoid food intake for at least 4 hours prior to the test. Patients with diabetes should get advice from the treating physician.
• Patients may be asked to stop taking drugs that can alter the test results for a few days prior to the test.
• Wear comfortable shoes and clothing
• Once all the information has been provided, the patient will be asked to sign a consent form.
How is it performed?
A stress echo is performed very much like an echocardiogram. However, there are 3 stages to the test:
• Resting echocardiogram
• Stress test – either a treadmill test, exercise bike, or drugs
• Repeat echocardiogram – when the heart is beating fast and hard
Resting echocardiogram
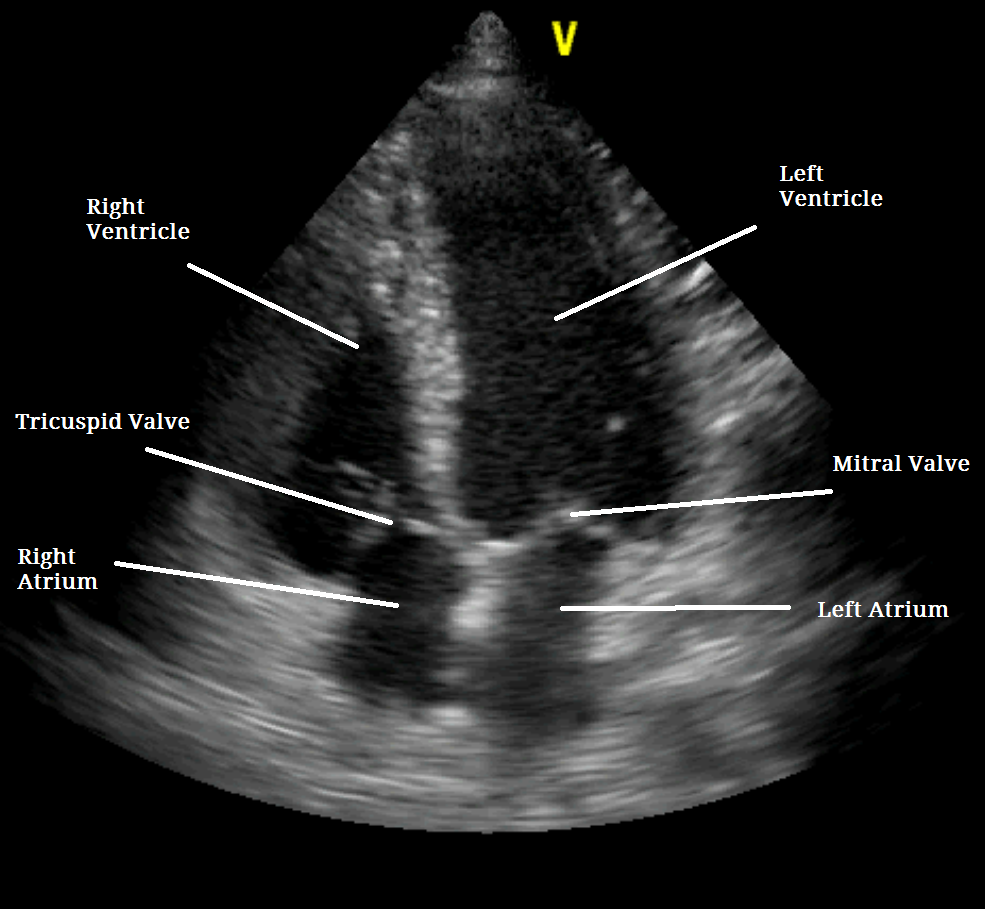
The resting echocardiogram is performed exactly like a normal echocardiogram. The patient is hooked up to the echo machine to monitor the heart, and images of the heart are taken and stored.
Stress test
This can be either a treadmill test, and exercise bike test or a test conducted using certain drugs that speed up the heart.
The treadmill exercise test has been discussed previously. The aim of the test here is to increase the heart rate in order to produce enough stress on it to alter its blood supply. The heart rate and blood pressure will be monitored closely by the physician. Once the heart rate is suitably elevated, the exercise is terminated and a repeat echo is performed.
When drugs are administered instead of performing the treadmill test, a small needle called a cannula is inserted into a vein in the arm, through which a drip is commenced. The drip contains a drug (e.g. dobutamine, adenosine) that is injected in controlled amounts into the vein, while continuously monitoring the patient. The drug increases the heart rate gradually and the drip is stopped once the heart rate is suitably high.
Repeat echocardiogram
With the heart rate still elevated, the patient is returned to the couch, and the heart is scanned again. During this scan, the physician will particularly notice whether any parts of the heart muscle are not moving well. This could indicate underlying problems with blood supply to that part of the heart.
The test takes around 1.5 to 2 hours to conduct, from start to finish. Once all the images are obtained, they are stored on a CD/DVD.
What information does the test provide?
The resting echocardiogram provides information on structure of the heart muscle, valves and the lining of the heart (pericardium). In particular, the resting scan reveals any abnormal movements of different parts of the heart muscle when it is in a relaxed state.
Upon exercise or administration of drugs, the heart rate increases. When the heart rate increases, it requires more blood for it to function optimally. This does not occur if the blood supply is compromised due to narrowing of heart arteries, and this is reflected by reduced or abnormal movements in the heart muscle. In addition to this, it can provide information on problems with the heart valves or blood flow across it under stress.
By providing this information, the doctor is able to decide what treatment, if any, is appropriate, and if any further tests are required.
Safety of the test
The test is relatively safe to perform. The patient may experience fatigue and breathlessness as is expected from the exercise test (on the treadmill or exercise bike). The test is continuously monitored by experienced technicians or a physician to handle any cardiac complications (like irregular rhythms, chest pains etc.) from the exercise tests. There are no risks associated with undergoing the heart scan.
Limitations
Though the test indicates as to whether the blood supplying the heart muscle is compromised, it does not indicate clearly as to which artery is narrowed and to what extent. The treadmill test cannot be performed in patients who have problems with mobility (arthritis, knee pain, ankle pain etc.). In such patients, the dobutamine test can be used. However, dobutamine stress test is avoided in patients with a history of irregular heart rhythms.
Stress echo tests are also avoided in patients suffering from a heart attack and in patients who are acutely ill. On the discretion of the physician, it may be avoided in patients with severely narrowed heart valves or with very weak hearts.
Your doctor will only recommend the test if it will aid reaching a diagnosis.
- Güncel Giriş Adresi, Hoşgeldin Bonusu - February 14, 2023
- “ставки На Спорт Онлайн Букмекерские Ставки и Футбол На следующий Прогнозы На Спорт Сделать Live Ставку На Спорт и Сайте Б - November 29, 2022
- Harburg-aktuell.de bietet Sportbegeisterten neue Wege zur Unterstützung ihrer Teams - April 26, 2022