Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a breakthrough technology that has changed the way patients with diabetes manage their condition.
In the recent past, I have been using this technology for a lot of my patients with diabetes.
This is because, unlike traditional blood glucose monitoring methods that provide readings occasionally, CGM offers real-time glucose measurements throughout the day and night, providing valuable insights into a patient’s glucose patterns.
In this article, I will explore what CGM is, why it is performed, how the test is conducted, how the results are interpreted, and the immense value it adds to the management of patients with diabetes.
What is Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring is a cutting-edge technology that enables the continuous monitoring of glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. It has been around for a while but is only recently being used a lot more frequently.
It involves the use of a tiny sensor placed on the skin, typically on the back of the arm, to measure glucose levels in the bloodstream. The sensor wirelessly transmits the data to a monitoring device or smartphone, where it can be analyzed in real-time.
Why is CGM performed?
Continuous Glucose Monitoring is performed to provide individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers with a comprehensive picture of their glucose patterns.
The primary goals of CGM are the following –
a) Monitor glucose levels
CGM allows for frequent monitoring of glucose levels, providing information on how blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day and night. This is evident in the picture below.
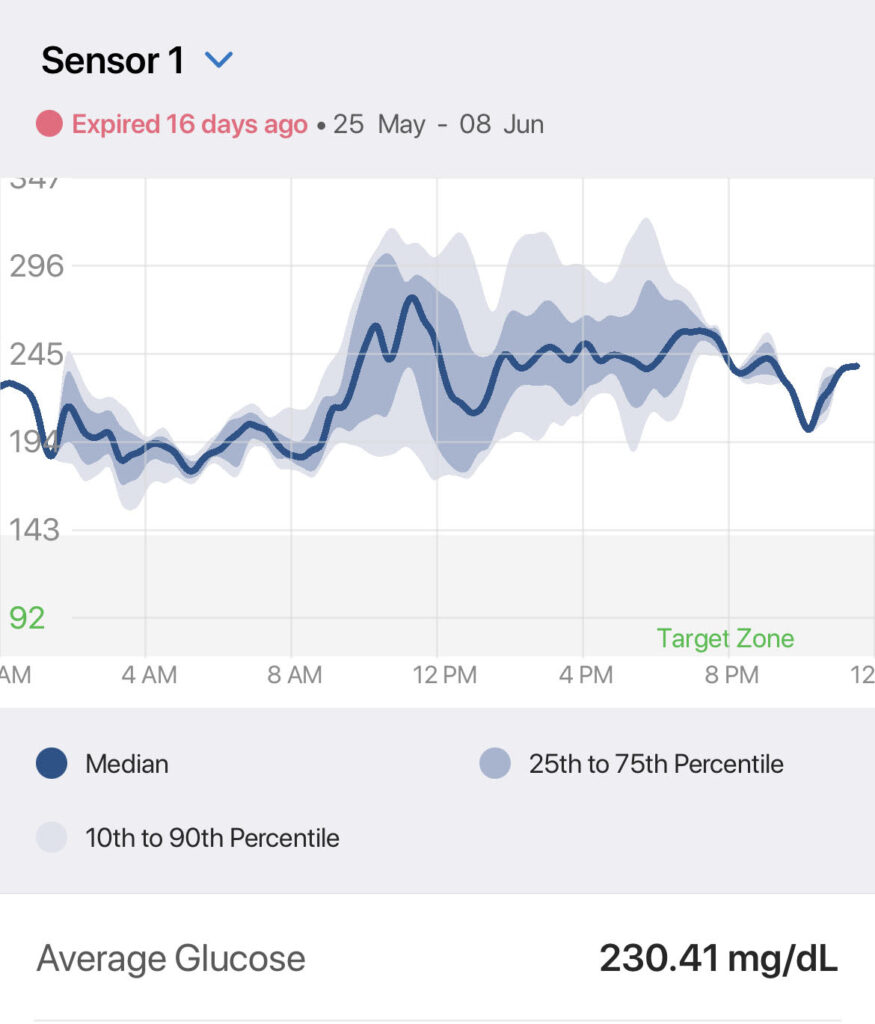
b) Identify trends and patterns
CGM data helps identify trends and patterns in glucose levels, such as post-meal spikes or nocturnal hypoglycemia, which may not be evident with traditional monitoring methods.
c) Optimize treatment
By providing real-time glucose data, CGM assists healthcare professionals in making informed decisions regarding medication adjustments, dietary modifications, and lifestyle changes to optimize diabetes management.
How Is The CGM Test Conducted?
The CGM test involves several steps that I have listed in the box below.
a) Sensor insertion: A small, flexible sensor is inserted on the skin using an applicator. The sensor contains a tiny wire that measures glucose levels in the interstitial body fluid.
b) Calibration: The CGM system typically requires calibration with a traditional fingerstick blood glucose reading to ensure accurate readings. This calibration is usually done when the sensor is first inserted and periodically throughout the wear time.
c) Data collection: The sensor wirelessly transmits glucose data to a receiver or smartphone app. Some systems provide real-time data, while others require periodic scanning of the sensor to download the data.
d) Data interpretation: The collected data is analyzed to identify glucose trends, patterns, and potential issues that need attention.
e) Sensor replacement: Depending on the device, the sensor may need to be replaced every few days or after a certain wear period. Usually, the sensors are applied for 14 days.
Interpreting CGM Results
CGM provides a wealth of information to healthcare professionals and individuals with diabetes.

a) Glucose trends
CGM allows for the identification of trends in glucose levels, such as high or low blood sugar patterns, overnight variations, and post-meal spikes.
b) Time in range
The time spent within the target glucose range (e.g., 90-180 mg/dL) is an essential metric in CGM analysis. It helps assess glycemic control and the effectiveness of diabetes management strategies.
c) Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia
CGM data provides insights into episodes of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), allowing for prompt intervention and adjustments to treatment plans.
d) Glucose variability
CGM also highlights the degree of glucose variability, indicating how much glucose levels fluctuate over time. Reducing variability can be beneficial in improving diabetes control and minimizing the risk of complications.
The Immense Value of CGM in Diabetes Management
Continuous Glucose Monitoring has brought about a paradigm shift in diabetes management, offering several significant benefits.
a) Early detection of glucose abnormalities
CGM allows for the early detection of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia episodes, enabling timely interventions and reducing the risk of acute complications.
b) Improved treatment decisions
Real-time access to glucose data empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed treatment decisions, including adjusting medication dosages, modifying dietary choices, and implementing lifestyle changes.
c) Enhanced glycemic control
By providing a more comprehensive view of glucose patterns, CGM helps individuals with diabetes achieve and maintain target glucose levels, thereby reducing the risk of long-term complications.
d) Lifestyle adjustments
CGM data highlights the impact of food choices, physical activity, stress, and other factors on glucose levels. This information aids patients in making lifestyle adjustments to improve diabetes management.
e) Reduced burden of fingerstick testing
At a particular point, finger prick testing constantly can become frustrating for patients. CGM significantly reduces the need for frequent fingerstick testing, making diabetes management less invasive and more convenient.
f) Insights into sleep patterns
CGM can uncover nocturnal hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, helping individuals understand the impact of sleep on glucose levels and take appropriate measures.
g) Data sharing and remote monitoring
CGM systems often allow for data sharing with healthcare providers, enabling remote monitoring and timely adjustments to treatment plans.
Conclusion
Continuous Glucose Monitoring has emerged as a game-changer in diabetes management.
By providing real-time glucose data and offering insights into glucose patterns, CGM empowers individuals with diabetes and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions and optimize treatment strategies.
As technology advances, CGM promises to improve glycemic control, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance the quality of life for millions of people living with diabetes.
CGM devices are available online on Amazon here.
- Understanding Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Guide for Patients - May 31, 2025
- CT Coronary Calcium Score: A Guide for Patients - January 7, 2024
- Gastric Antral Vascular Ectasia (GAVE) – Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment - August 5, 2023

